Regardless of whether you’re a professional photographer, videographer, or just a regular person using a camera, selecting the right lens for your project is crucial. are numerous lenses available for purchase, however, you cannot afford to be unsure of which lens to choose.
To get the frame with the desired perspective, a correct choice of lens is more than half the battle won. This single choice can elucidate a viewer if you are a professional or amateur. So let’s first understand what is a lens, fundamentals and science behind it, types of lenses and which one should you buy.
Table of Contents
A camera lens is an optical body that consists of a series of lenses mounted in such a way that refracts the photons (light rays) and converges them in order to focus on a photosensitive surface (sensor) of the camera.
Four key characteristics set certain lenses apart from one another: aperture, focal length, autofocus, and image stabilization. We’ll attempt to comprehend each of these separately as how they relate to the lens and the resulting image.
Aperture
An aperture is a hole or opening in the lens’ diaphragm that serves as the entrance point for light. In simple words, the opening through which photons (light) pass to enter the camera. The opening can be made bigger or smaller subsequently, allowing us to adjust the amount of light that enters. We can adjust the exposure of our final image in this way.
This is a component of the exposure triangle(Aperture, ISO, and shutter speed), which serves as an illustration of the key components in the creation of images.
Is serves two responsibilities in a camera: it controls he exposure (brightness) and depth of field which allows you to increase or decrease the blurriness of the background or foreground which is out of focus.
Read more about Aperture in this post about exposure triangle
Focal length
Focal length is the distance between the point of convergence of light in the lens and the surface of sensor, It is responsible for capturing images of a certain angle of view. Different focal length brings you images of a different angle of view like wide/ultra wide angle, closeup, and different scale of magnification as well. Smaller the focal length, the wider the image would be; the Larger the focal length, the shallower the angle of view would be giving you a closer-up, magnified image.
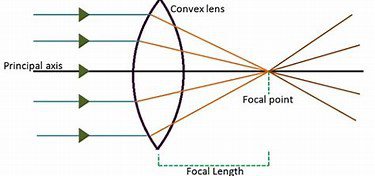
Let’s understand focal length in the language of physics, the incoming rays are the photons (or light particles) that have been reflected through certain objects and now incidents at the lens the point where they started bending till the point they all met the surface of your camera sensor(focal point) is the focal length.
Now if we move the lens farther i.e increase the focal length it would not be able to collect the incident rays that are currently in the corner and only refract light that is close to the centre. As a result, the object is magnified from its original size ratio and a closeup photograph.
Focusing
To get a sharp and clear image of our subject, the focal point must be on the surface of the camera sensor, but a fixed focal length can only focus on a predefined distance, requiring you to move far or near the subject to keep in focus and the rest blurred, which is more difficult and complicated, and we would not be allowed to get our desired frame from the desired distance. To combat this issue, camera lens body manipulates refraction by adding more lenses inside, which increases or decreases light bending and hence the focal point too. This allows us to focus on varying distances while maintaining the same focal length. This way, we can change the focus to different distances without changing our frame
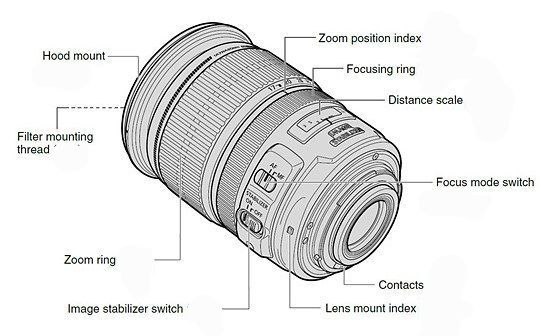
We get a focus ring on the lens body that we can use to change the focus, but most lenses also have autofocus, which means that the camera guesses the subject and shifts its focus there using its intelligence.
Note: The default focal length of a lens is measured and defined keeping its focus to infinity.
Types of lenses
Lenses can be classified and subclassified in this way :
- Prime lens- Lenses with a fixed focal length where you can not optically zoom into the frame. But they are faster and sharper than other lenses and lightweight too. That’s why every photographer loves the prime lens despite its limitations.
2. Zoom lens- a series of lenses that allow different focal lengths from a single lens, making them more versatile but less fast and sharp than prime lenses. Every advantageous property comes with compromise as well.
These are other diverse classifications of lenses inside of prime and zoom lenses :
- Wide angle lenses: These lenses have a smaller focal length than 50mm, providing a wider angle of view. These lenses are ideal for landscapes and interior shoots. Click here to see examples.
- Telephoto lenses: These lenses have a longer focal length, a very tight and closed angle of view, and more magnification. These capture more zoomed-in pictures than those of a wide-angle lens. Click here to see examples.
- Standard lenses: Sort of allrounder lenses that lie somewhere between wide-angle and telephoto lenses. If you have a standard zoom lens you can achieve enough wide and closeup frames at the same time from this single lens only. The focal length of standard lenses rules somewhere between 35mm to 85mm. Click here to see examples.
- Macro lenses: These lenses are used to capture extreme closeup, and macro photographs and have a very short focal length. You can use these lenses to capture minute details in nature or small insects from such extreme closeup that is not even noticeable through a human eye.
- Tilt-shift lenses: This is a very different kind of lens, which after getting mounted to the camera, can shift its body in a way that changes the position of the lens in relation to the camera. This is most useful in architectural photography because it provides a wider-angle image without any distortion. for example, you can say a panoramic picture without perspective distortion, because it can go parallel to the image by tilting itself without moving the camera. That means you can take picture of something at a higher angle by keeping your camera pointed straight only.
- Fisheye lens: These are ultra-wide angle lenses that can provide you an angle of view of more than 180°. You get a distorted image that looks like a fisheye or a bubble and this is usually used to show some creativity.

Common lenses sizes and specs
| Focal length | The angle of view and characteristics | Best usage |
|---|---|---|
| 1. 16mm | Very wide; A little distortion; Almost everything in focus | Landscapes; shooting in compact spaces |
| 2. 50mm | standard angle, closest to the angle of view to that of a human eye; No distortion | Usable in almost all types of shoots; Portraits with good Depth of field |
| 3. 70-200mm | Medium to telephoto; to shoot from a good distance; magnified subject and background | Portraits, wildlife |
| 4. 85mm | Medium telephoto; No distortion; Sharp and shallow depth of field | Portraits; Product shoots |
| 5. 35mm | Wide; No distortion; | Street photography; Weddings; interviews |


Russian @ 600 only?
Impressive posts! My blog Webemail24 about SEO also has a lot of exclusive content I created myself, I am sure you won’t leave empty-handed if you drop by my page.
gambar tabel shio 2023
Ahaa, its nice conversation about this article at this place at this web site, I have read all that, so at
this time me also commenting here.
I’ve been browsing online more than 2 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally,
if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you
did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
rajabandot rajabandot rajabandot
Highly descriptive post, I loved that bit.
Will there be a part 2?
protogel protogel protogel
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post.
Many thanks for supplying this info.